Mapping of ICD-9 to ICD-10
One of the identified benefits for the United States' transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 is because of the increased level of specificity offered by the ICD-10 code format. This specificity will benefit patients and doctors (by giving more detailed diagnosis and treatment information), payers (by more accurately defining services) and international organizations that monitor worldwide disease.
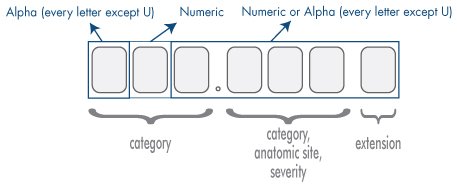
However, all of this increased specificity comes at a price—the codes are becoming more complex. In ICD-9-CM, codes are three to five digits. The first digit is either numeric or alpha (the letters E or V only) and all other digits are numeric.
In ICD-10-CM, however, codes can be up to seven digits. The first digit is always alpha (it can be any letter except U), the second digit is always numeric, and the remaining five digits can be any combination.
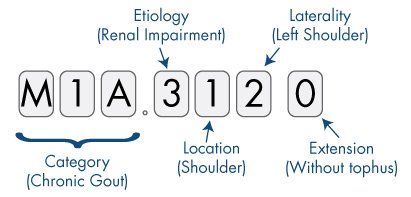
The following example shows an ICD-10-CM code for chronic gout due to renal impairment, left shoulder, without tophus.
The corresponding ICD-9-CM code would have been 274.02, which only indicates gouty arthropathy. As you can see, the ICD-10-CM code contains much more information.
Mapping
Some ICD-9-CM codes map easily to ICD-10 in a simple one-to-one conversion. For example, the ICD-9-CM code 733.6 (Tietze's Syndrome) maps directly to the ICD-10-CM code M94.0. (An exact map does not always mean the codes match in detail.)
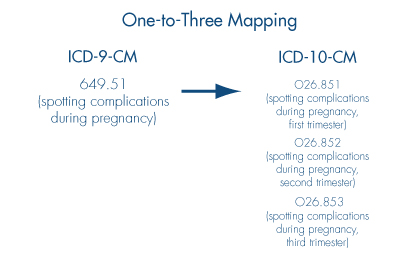
Other codes will require additional information to map for possible solutions. For example, the ICD-9-CM code 649.51 (spotting complicating pregnancy) requires information about weeks in pregnancy to map. There are three options: O26.851 (spotting complicating pregnancy, first trimester), O26.852 (spotting complicating pregnancy, second trimester), and O26.853 (spotting complicating pregnancy, third trimester).
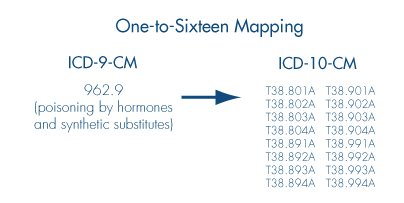
And some codes require significantly more specificity and map into many more ICD-10-CM code set selections. For example, the ICD-9-CM code 962.9 (poisoning by hormones and synthetic substitutes) has sixteen corresponding ICD-10-CM codes, requiring information about both the cause of the poisoning and the type of encounter.
In an extreme example, the ICD-9-CM code 733.82 (other disorders of bone and cartilage, nonunion of fracture) there are 2530 corresponding ICD-10-CM codes due to the degree of specificity required in ICD-10.
ALERT:
The fact is : No true crosswalk' exists between ICD-9
and ICD-10
For help with understanding ICD-10 and converting codes,
refer to our AccuChecker Online ICD-10 code conversion tool, see our ICD-9 to
ICD-10
For more
information on AccuChecker Online or our services:
786-231-7585 or 1-877-938-9311



No comments:
Post a Comment